September 2019
Principality of Monaco is world’s first country to have full, operational 5G coverage!
With the roll-out of 5G, the Prince’s Government is building the first pillar of its Extended Monaco programme. The aim is to bring the Principality into the digital age.

Since 9 July 2019, individuals and businesses in Monaco have been able to access the new 5G technology, which opens up new opportunities that make everyday life easier for those who live or work in Monaco, and for visitors to the country.
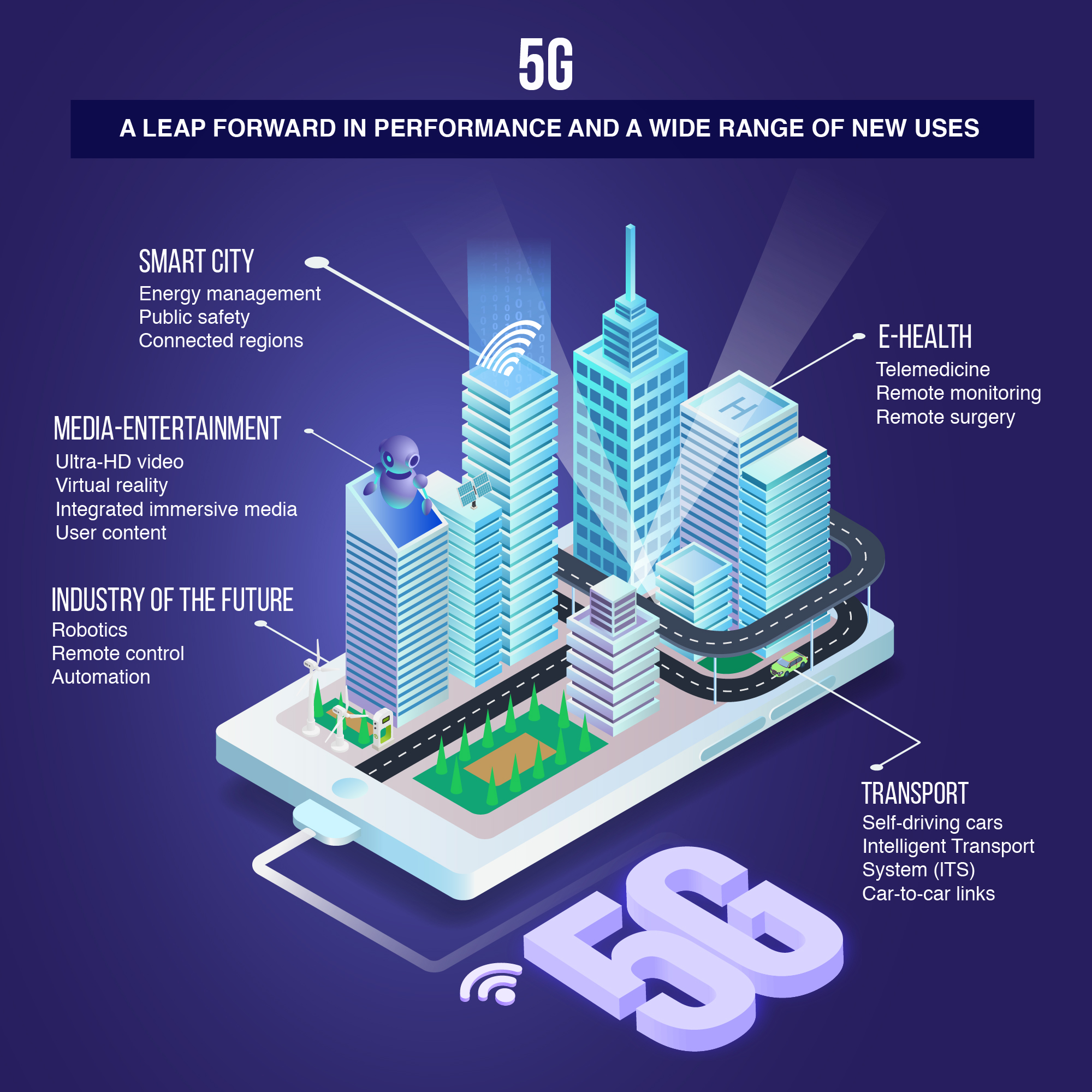
- Smart bus shelters now offer public Wi-Fi via the 5G network. They will also soon feature new services supported by environmental sensors.
- Monaco’s Fire and Emergency Service plans to use 5G to better protect the population: firefighters are getting ready to use surveillance drones equipped with high-definition cameras as well as a pre-diagnostic app that is linked to the hospital and can be used at the scene of an accident to save time and improve victims’ chances of survival.
- Self-driving vehicles (which have been trialled in the Principality) will include 5G technology in future versions.
- For companies based in Monaco, the 5G roll-out also opens up functionality that will help to generate new markets. For example, Teale, a start-up working with the Principality’s start-up programme MonacoTech and which specialises in intelligent building management, has demonstrated the contribution 5G can make to remote control of facilities in order to improve energy efficiency.
5G is not simply an improved version of 4G, it represents a paradigm shift.
Frédéric Genta, Country Chief Digital Officer
The opportunities associated with 5G are huge, still difficult to qualify and quantify, and different from those of previous generations. The technology behind 5G makes it possible to expand its scope (notably by connecting objects) and will have an impact on the pillars of our society and our economy. Energy, health, the media, industry and transport will all enter a new era. This is therefore a true step forward for the Principality, its residents, its public policies and its economy.
Monaco is the first country to enjoy 100% coverage by a commercial 5G network, with other countries such as South Korea, the United States, the United Kingdom and Spain having rolled the technology out only to select pilot cities.
The 5G standard offers significant technical improvements in three areas: speed, latency and density.
1/ Substantially increased speed, making it possible to achieve a level equivalent to fibre with users enjoying speeds of at least 100 Mbits/s and up to a maximum of 20 Gbit/s.
These speeds are required by the changes in use: 4K video is becoming more widespread, 8K is on the way, streaming has become the norm for video and will increase in popularity in ever more areas, including cloud gaming and virtual reality. These are all uses that demand more speed to eliminate the barrier, which should no longer exist, between our fixed and mobile devices.
2/ Much lower latency: 5G reduces latency from 10 ms to 2 ms, opening up opportunities for self-driving cars and drones as well as in medicine and remote surgery.
3/ In terms of density, 5G makes it possible to connect a high number of devices per square kilometre, something which is key to the Internet of Things, particularly when it comes to smart homes and the Monaco Smart City goal.
5G is a major innovation.
Martin PERONNET, Managing Director of Monaco Telecom
Monaco Telecom is offering a strong response to the new uses and demands from residents for fast mobile access with a high level of density, by introducing a technology that will soon become indispensable. In addition to supporting the development of the #ExtendedMonaco programme, 5G in the Principality will allow unique services to be offered to local residents that are visible in users’ everyday lives within the Smart City.
At the same time, Monaco Telecom is continuing to roll out the fibre network in order to provide businesses and individuals with an exceptional level of service.
Regulations that exceed international standards
As a precaution and in anticipation of residents’ concerns, in 2010 the Principality drew up a prevailing regulatory framework on electromagnetic fields, strengthening the international standard published by the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP), which establishes recommendations on maximum public exposure levels. These limits are 50 times lower than the level which produces initial thermal effects, and they have been reduced further still in Monaco. To improve transparency, the Government will also publish an electromagnetic map and a map of antenna locations by the end of the year.
Alexandre Bordero, the Government’s Director of Health Affairs, has also issued a message to reassure residents, reiterating the opinions of the World Health Organisation (WHO) and ANSES in France. Having reviewed all of the joint international scientific studies on electromagnetic waves which have been published and audited over the last 20 years, 5G technology, just like 3G and 4G, has been determined to present no new health risks.
In addition, the techniques that 5G uses to emit waves results in a lower degree of dispersion compared with previous technologies such as 2G, 3G and 4G. The phasing out of these previous generations of mobile networks in favour of 5G is likely to lead to a reduction in the average electromagnetic field to which people are exposed, given the same amount of use.


